Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
Rack pinion systems are essential components in various mechanical applications. They convert rotational motion into linear motion efficiently. The mechanism consists of a round gear (the pinion) that engages with a flat, toothed bar (the rack). This design is prevalent in steering systems, elevators, and machinery.
Understanding how rack pinion works is vital. It offers precise control and positioning. For instance, in cars, the steering wheel turns the pinion, which moves the rack. This movement directs the wheels. The simplicity of this system is appealing, yet it requires careful maintenance. Over time, wear can affect performance.
It is interesting to note that while rack pinion systems are effective, they can present challenges. Misalignments or damaged teeth can cause issues. Minor errors may lead to significant performance drops. Therefore, proper installation and regular checks are necessary. While they are generally reliable, operator awareness is crucial to prevent failures.
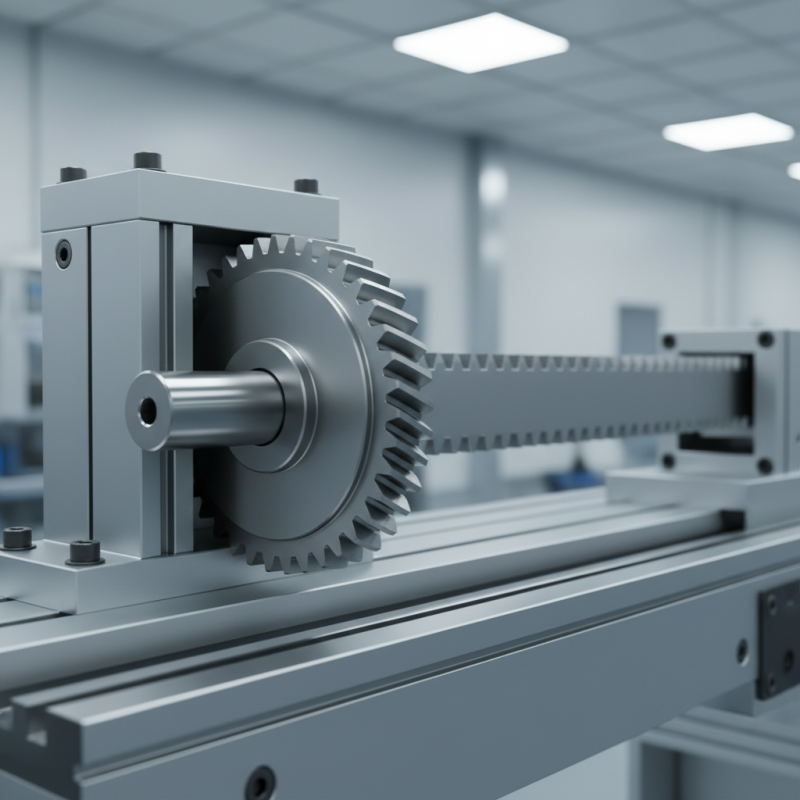

Rack and pinion is a mechanism widely used in mechanical systems. Its components include a flat bar called the rack and a round gear known as the pinion. The rack has teeth that mesh with the pinion. When the pinion rotates, the rack moves linearly. This simple yet effective design converts rotational motion into linear motion.
Components of the rack and pinion must be precisely created. Flaws in the gearing can cause slipping or noise during operation. Maintenance is crucial to avoid wear and tear. Over time, dirt and debris can accumulate, impacting performance. Regular checks ensure smooth operation.
This system is common in steering gears of vehicles and various machines. However, it requires careful consideration in design to handle loads effectively. Sometimes, engineers overlook the size of components, leading to inefficiencies. Adjustments may be necessary to improve function. Understanding the intricate details of rack and pinion can provide insights into optimizing mechanical systems.
The rack and pinion system is an essential mechanical principle. It converts rotational motion into linear motion. The setup consists of a gear (the pinion) that meshes with a linear toothed bar (the rack). When the pinion rotates, the teeth engage the rack, moving it in a straight line. Simple, yet effective, this system finds applications in steering mechanisms and machinery.
For designers, precision is critical in this system. The alignment of teeth affects performance. Misalignment can cause wear and reduce efficiency. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure smooth operation. Check the condition of both rack and pinion periodically.
Tips: Always use lubrication. It reduces friction and wear. Inspect the teeth for damage frequently. Replace any worn parts to maintain functionality. A well-maintained rack and pinion system can provide years of reliable service.
| Component | Description | Material | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rack | Linear gear that translates rotational motion into linear motion. | Steel or aluminum | Steering systems, machine tools, and linear actuators. |
| Pinion | Small gear that engages with the rack to convert rotary motion to linear motion. | Steel or plastic | Robotic arms, elevators, and automated guided vehicles. |
| Gear Ratio | The ratio of the number of teeth on the pinion to the number of teeth on the rack. | N/A | Determines speed and torque in applications. |
| Mounting | The method by which the rack and pinion are secured in machines or vehicles. | Various options available (bolts, brackets). | Industrial machinery, automotive systems. |
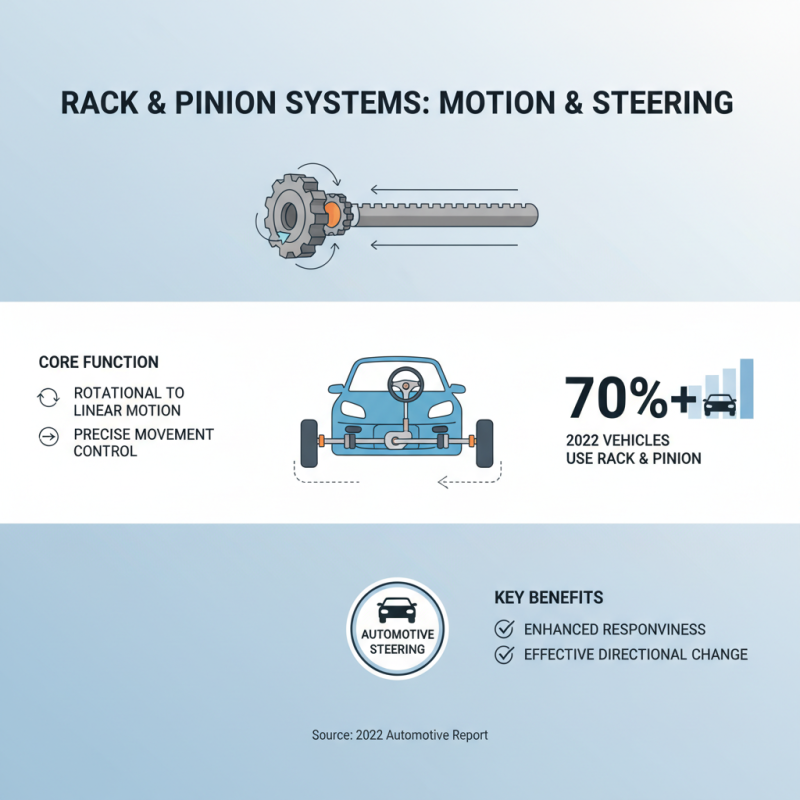
Rack and pinion systems play a vital role in various industries. They provide precise linear motion from rotational movement. In automotive applications, they are crucial for steering systems. According to a 2022 report, over 70% of vehicles use rack and pinion for steering. This design enhances responsiveness and changes vehicle direction effectively.
In manufacturing, rack and pinion systems drive conveyor belts and CNC machines. Their ability to convert rotary motion into linear movement is indispensable. Data suggests that around 45% of manufacturing firms rely on this mechanism for their automation processes. This reliance is often driven by the need for high precision. However, some systems show wear over time. Regular maintenance is essential but often overlooked, leading to performance issues.
Furthermore, rack and pinion have applications in robotics. They allow for efficient arm movements during assembly tasks. Insights indicate that over 40% of robotic arms incorporate this mechanism. Yet, design flaws can result in alignment issues, affecting efficiency. Despite their advantages, users must consider these challenges to optimize performance.
Rack and pinion mechanisms play a vital role in various mechanical systems. They convert rotational motion into linear motion. This efficiency makes them popular in steering systems and conveyor mechanisms. By using a cylindrical gear (the pinion) and a flat bar with teeth (the rack), they create smooth, controlled movement.
One major advantage is their simplicity. Fewer components mean lower costs and easier maintenance. These systems are also compact, which is essential for space-constrained applications. They can handle substantial loads despite their size. This characteristic makes them ideal for heavy machinery and moving parts in different environments.
Despite their advantages, there are aspects to consider. For instance, wear and tear occur over time, affecting performance. Precision is crucial; otherwise, misalignment can lead to inefficient operation. Proper installation and regular checks are essential to avoid issues. Balancing maintenance efforts with performance is necessary for longevity.
Rack and pinion systems play a crucial role in various mechanical applications. Regular maintenance ensures their efficient performance. According to industry reports, approximately 40% of machinery failures are linked to improper maintenance practices. This statistic highlights the need to inspect gears, lubrication, and alignment frequently.
During maintenance, check the gear teeth for wear and tear. A worn tooth can lead to faulty operation. It's essential to lubricate the system adequately. Insufficient lubrication can result in increased friction and heat. This may reduce the lifespan of the parts. Reports also suggest that maintaining proper alignment can enhance performance by up to 30%. Misalignment often goes unnoticed until significant issues arise.
Troubleshooting requires a systematic approach. Listen for unusual noises during operation. They may signal a problem with the gears. Vibrations can also indicate misalignment or wear. Furthermore, keeping a log of maintenance activities can help identify patterns over time. This data is valuable in predicting future issues. Frequent checks can prevent costly repairs and downtime.